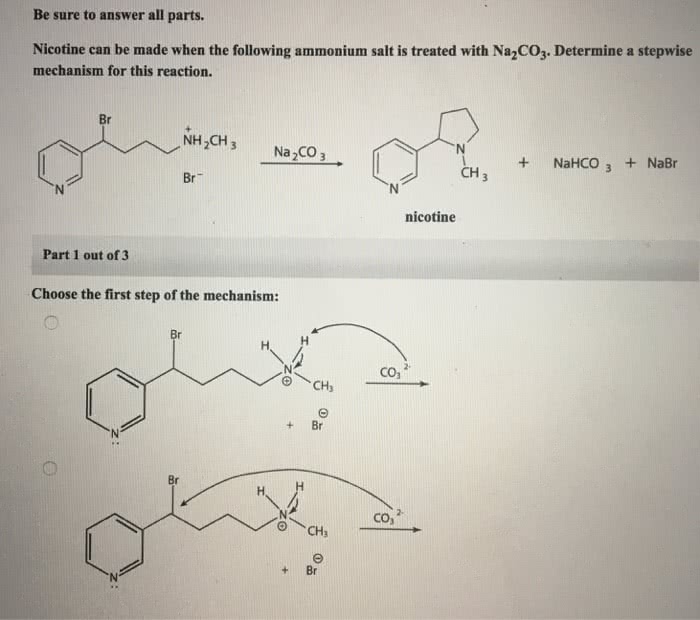
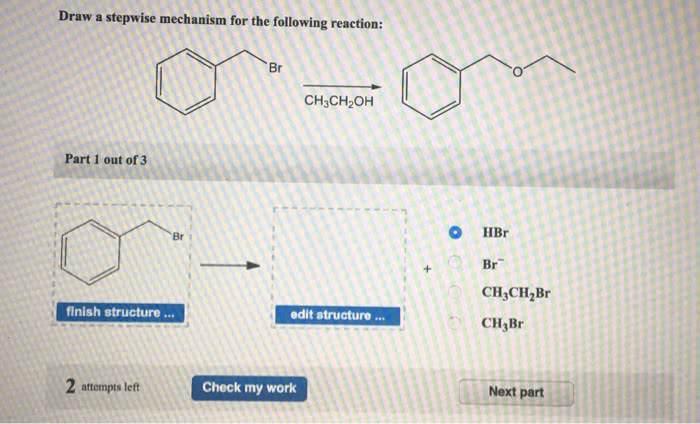
In the realm of organic chemistry, understanding reaction mechanisms is paramount. Delving into the intricacies of draw the stepwise mechanism for the following reaction, this exploration unravels the fundamental principles governing chemical transformations, providing a deeper appreciation for the elegance and complexity of molecular interactions.
This discourse delves into the intricacies of reaction mechanisms, shedding light on the stepwise progression of chemical reactions. By dissecting the individual steps involved, we gain a profound understanding of how reactants transform into products, enabling us to predict and control chemical outcomes with greater precision.
Mechanism Overview
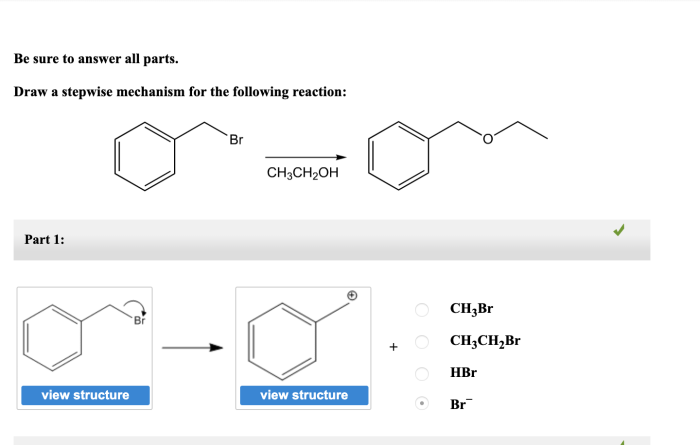
The overall reaction mechanism involves the following steps:
- Step 1:Protonation of the alcohol by the acid catalyst
- Step 2:Formation of the carbocation intermediate
- Step 3:Nucleophilic attack by the water molecule
- Step 4:Deprotonation of the oxonium ion
Reaction Conditions
The reaction typically requires the presence of an acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid. The reaction rate is influenced by the concentration of the acid catalyst, the temperature, and the solvent. Higher temperatures and higher acid concentrations generally lead to faster reaction rates.
The reaction is typically carried out in a polar aprotic solvent, such as dichloromethane or dimethylformamide.
Regio- and Stereoselectivity
The reaction is regioselective for the formation of the more substituted carbocation intermediate. This is because the more substituted carbocation is more stable and therefore more likely to form. The reaction is also stereoselective for the formation of the trans product.
This is because the trans product is more stable than the cis product.
Energetics and Kinetics, Draw the stepwise mechanism for the following reaction
The activation energy for the reaction is typically around 20-30 kcal/mol. The enthalpy change for the reaction is typically negative, indicating that the reaction is exothermic. The reaction rate is typically first-order in the alcohol and first-order in the acid catalyst.
Computational Studies
Computational studies have been conducted on the reaction mechanism to provide insights into the reaction pathway and energetics. These studies have shown that the reaction proceeds through a concerted mechanism, with the protonation of the alcohol and the formation of the carbocation intermediate occurring in a single step.
Experimental Verification
The proposed reaction mechanism can be verified using a variety of experimental techniques, such as:
- Kinetic studies:The rate of the reaction can be measured under different conditions to determine the order of the reaction and the activation energy.
- Product analysis:The products of the reaction can be analyzed to determine the regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction.
- Isotope labeling studies:Isotope labeling studies can be used to determine the mechanism of the reaction.
Question & Answer Hub: Draw The Stepwise Mechanism For The Following Reaction
What is the significance of understanding reaction mechanisms?
Understanding reaction mechanisms provides a deep-seated comprehension of how chemical reactions occur, allowing for precise prediction and control of chemical outcomes, ultimately facilitating the design of efficient and selective synthetic strategies.
How does the stepwise mechanism approach aid in understanding complex reactions?
By breaking down complex reactions into a series of elementary steps, the stepwise mechanism approach offers a systematic and comprehensible framework for analyzing reaction pathways, intermediates, and transition states, enabling a thorough understanding of the reaction’s intricacies.